What's Next for Space Exploration: The Future?
Private space exploration is experiencing a renaissance. Reusing rocket stages can reduce the cost of space travel, as demonstrated by businesses like SpaceX and Blue Origin. However, being a national organization, NASA depends on the public's support to maintain its momentum. Few Americans believe that sending people to Mars should be the agency's top goal, but those who do list tracking asteroids that might strike Earth and keeping an eye on the planet's climate system as high objectives.
Moon
Mars
 NASA plans to return humans to the moon in 2024, more than 50 years after the moon race. The mission will assist in laying the groundwork for a crewed trip to Mars.
Additionally, private businesses have been creating their own spacecraft. Since many of these vehicles may be used again, space travel is less expensive.
Numerous Americans perceive an increasing role for commercial space exploration firms with private leadership to carry out manned space missions up to and including orbit. Indeed, seven out of ten Americans believe that the US must remain in the forefront of space development.
Researchers are hopeful that upcoming rovers may be able to discover indications of Martian life. These expectations are predicated on technological advancements that enable the detection of minute molecules produced by living or deceased creatures. By applying the knowledge gained from the hunt for life on Earth, other scientists are creating techniques to find organic compound residues and other signs of extant or former life on Mars.
NASA plans to return humans to the moon in 2024, more than 50 years after the moon race. The mission will assist in laying the groundwork for a crewed trip to Mars.
Additionally, private businesses have been creating their own spacecraft. Since many of these vehicles may be used again, space travel is less expensive.
Numerous Americans perceive an increasing role for commercial space exploration firms with private leadership to carry out manned space missions up to and including orbit. Indeed, seven out of ten Americans believe that the US must remain in the forefront of space development.
Researchers are hopeful that upcoming rovers may be able to discover indications of Martian life. These expectations are predicated on technological advancements that enable the detection of minute molecules produced by living or deceased creatures. By applying the knowledge gained from the hunt for life on Earth, other scientists are creating techniques to find organic compound residues and other signs of extant or former life on Mars.
Station Space
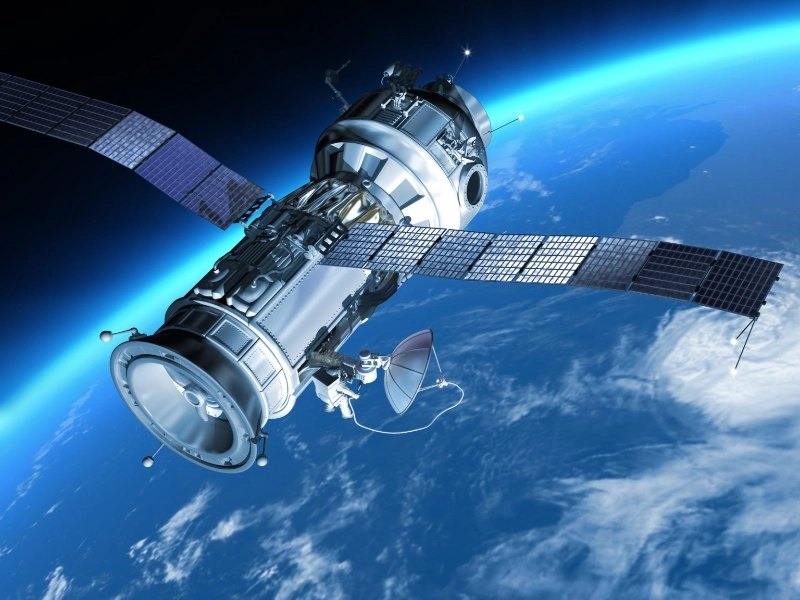 Since Earth and other planets are so far apart astronomically, most physical exploration beyond our solar system is still done by robots. However, there is hope that humanity will be able to visit Mars and other planets in the future. Private businesses like SpaceX and government organizations like NASA and ESA are developing novel technologies that could lower the price of interplanetary travel.
There may be several noteworthy space missions this year. In October, a spacecraft named Psyche is scheduled to launch to visit 16 Psyche, a unique metal world. Additionally, the icy moons of this gas giant will be studied by a spacecraft named Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer that will be launched.
Because reusable rockets will make space journeys more affordable, people will be able to take tourist trips into low-Earth orbit. Furthermore, a new generation of potent telescopes, such as the James Webb Telescope, will expand our understanding of the universe and its stars. With the use of technology, we will be able to detect dark matter, see the unseen, and look for evidence of extrasolar life.
Since Earth and other planets are so far apart astronomically, most physical exploration beyond our solar system is still done by robots. However, there is hope that humanity will be able to visit Mars and other planets in the future. Private businesses like SpaceX and government organizations like NASA and ESA are developing novel technologies that could lower the price of interplanetary travel.
There may be several noteworthy space missions this year. In October, a spacecraft named Psyche is scheduled to launch to visit 16 Psyche, a unique metal world. Additionally, the icy moons of this gas giant will be studied by a spacecraft named Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer that will be launched.
Because reusable rockets will make space journeys more affordable, people will be able to take tourist trips into low-Earth orbit. Furthermore, a new generation of potent telescopes, such as the James Webb Telescope, will expand our understanding of the universe and its stars. With the use of technology, we will be able to detect dark matter, see the unseen, and look for evidence of extrasolar life.
Commercial Spacecraft
 There's a growing likelihood that robots, or at the very least autonomous vehicles operating without human pilots, will conduct space exploration. For instance, NASA's Curiosity vehicle is currently trundling across Martian craters and might uncover shocking information that human geologists would overlook. In the meantime, sensor technology is getting smaller and machine learning is advancing quickly.
Future space exploration will also be impacted by the commercialization of space. Tourists may already experience zero gravity and breathtaking vistas of Earth from orbit by boarding a private spacecraft, thanks to firms like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin.
In order to lay the basis for the 2024 Artemis mission, which would send humans to explore a lunar base and potentially search for water ice, NASA's Orion spacecraft will launch unmanned to the moon this year. The JUICE mission of the European Space Agency will arrive at Jupiter in 2023 and spend three and a half years studying Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto, the planet's moons.
There's a growing likelihood that robots, or at the very least autonomous vehicles operating without human pilots, will conduct space exploration. For instance, NASA's Curiosity vehicle is currently trundling across Martian craters and might uncover shocking information that human geologists would overlook. In the meantime, sensor technology is getting smaller and machine learning is advancing quickly.
Future space exploration will also be impacted by the commercialization of space. Tourists may already experience zero gravity and breathtaking vistas of Earth from orbit by boarding a private spacecraft, thanks to firms like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin.
In order to lay the basis for the 2024 Artemis mission, which would send humans to explore a lunar base and potentially search for water ice, NASA's Orion spacecraft will launch unmanned to the moon this year. The JUICE mission of the European Space Agency will arrive at Jupiter in 2023 and spend three and a half years studying Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto, the planet's moons.








